Heartwarming Tips About CAN A Bus With 60 Ohm Termination

Understanding Bus Termination
1. What's This "Bus" Thing, Anyway?
Let's not picture a vehicle full of passengers here, alright? In the world of electronics, a "bus" is more like a highway for digital signals. Think of it as the interconnected pathways that allow different components in a system — like your computer or a complex industrial machine — to chat with each other. These pathways carry data, instructions, and all sorts of crucial information. It's vital that this "conversation" happens smoothly and accurately.
Now, if signals encounter problems during their journey along this bus, you get errors, slowdowns, or even complete system crashes. And nobody wants that! That's where termination comes into play. It's like the traffic management system for your digital highway, ensuring everything flows smoothly.
Imagine a perfectly straight, smooth highway with clear signs. That's what we want for our signals. But sometimes, things aren't perfect. Signals can bounce around, reflect off the ends of the bus, and generally cause chaos. These reflections can interfere with the original signals, leading to data corruption. Termination is all about preventing these reflections.
Different types of buses exist, each with its own characteristics and requirements. Factors such as the bus's length, the speed of the signals, and the type of communication protocol used all play a role in determining the optimal termination strategy. Which leads us neatly to the topic of this whole thing: 60 ohms!

What Is Can Bus Wiring
Sixty Ohms
2. Why 60 Ohms, Specifically?
So, what's the deal with 60 ohms? Well, it's a specific impedance value used for termination in certain types of buses. "Impedance," in this context, is like the resistance that the bus presents to the signal. The idea behind termination is to match the impedance of the terminator resistor to the characteristic impedance of the bus. If they match, the signal gets nicely "absorbed" instead of reflecting. Think of it like a perfect catch in baseball, smooth, clean, and efficient!
The reason 60 ohms is chosen isn't arbitrary. It's usually determined by the specific standards and specifications of the bus system being used. For example, certain types of network communication standards, or specialized industrial control systems might require this impedance value for proper operation. Using the wrong impedance value can lead to those dreaded signal reflections, causing havoc and frustration.
Imagine trying to use a USB-C charger on a device designed for micro-USB. It simply won't work correctly, and you might even damage something! Similarly, mismatched termination can cause subtle but devastating issues within the bus system, leading to intermittent errors or a complete system breakdown over time.
Therefore, if a specific bus system requires 60-ohm termination, you absolutely need to use a terminator resistor with that value. Deviation from the standard is generally a recipe for disaster.

Customized CAN Bus With 120 Ohm Terminal Resistance Suppliers
Can a Bus Function with 60 Ohm Termination? The Heart of the Matter
3. The Short Answer (with a Little Caveat)
The direct answer is: YES, a bus can function with 60 ohm termination... if it's designed to. Let's be clear: a 60-ohm terminator won't magically work on any bus. It must be a bus specifically designed or requiring 60-ohm termination. This is a crucial point! Throwing a 60-ohm resistor at a random bus and hoping for the best is not a good strategy. It's like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole — it just won't work, and you'll probably break something in the process.
When a bus is designed for 60-ohm termination, the signal path and components are engineered to have a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. The terminator resistor is then placed at the end(s) of the bus to absorb the signal and prevent reflections. This ensures that the signals travel cleanly and reliably across the bus. It's all about creating a harmonious electrical environment.
Without the correct termination, signals might bounce back and forth, creating interference patterns that distort the intended message. These distortions can lead to errors in data transmission, resulting in glitches, crashes, or unpredictable behavior. Think of it like trying to listen to someone speaking in a room with a lot of echoes — it becomes difficult to understand what they're saying.
Proper termination is often dictated by industry standards or manufacturer specifications. Always consult the documentation for your specific bus system to determine the correct termination method and impedance value. Ignoring these guidelines can have serious consequences, leading to system instability and potential hardware damage. Always RTFM (Read The Fabulous Manual)!

Customized Terminal Resistor 120 Ohm, DB9, CAN Bus Suppliers
When 60 Ohms Isn't the Answer
4. Recognizing the Signs
Alright, so you're working with a bus system and things aren't running smoothly. How do you know if 60-ohm termination is the problem (or not the problem)? A common clue is intermittent errors — those frustrating issues that pop up seemingly at random, then disappear just as mysteriously. These can be caused by signal reflections interfering with the intended data.
Another sign could be a significant slowdown in data transfer rates. If the bus is constantly having to retransmit data due to errors, it's going to take longer to complete tasks. It's like trying to drive on a highway with constant stop-and-go traffic — you'll eventually get there, but it'll be a lot slower and more frustrating.
Complete system crashes, while not always indicative of termination problems, can also be a symptom. Signal reflections can sometimes be so severe that they completely disrupt the operation of the bus, causing the entire system to shut down.
But remember, these symptoms can also be caused by other issues, such as faulty cables, bad connectors, or even software glitches. Therefore, it's important to approach troubleshooting systematically and rule out other potential causes before focusing solely on termination. Don't go blaming the 60-ohm resistor right away!

The Takeaway
5. A Final Word of Ohm-ly Wisdom
So, the critical point is this: a bus can function with 60-ohm termination, if it's designed for it. Using the correct termination impedance is essential for reliable data transmission and system stability. Always consult the documentation for your specific bus system to determine the appropriate termination method. And if you're experiencing problems, don't just blindly slap a 60-ohm resistor on and hope for the best. Take a systematic approach to troubleshooting and ensure that you're addressing the root cause of the issue.
Think of it like baking a cake. You can't just throw in random ingredients and expect it to turn out perfectly. You need to follow the recipe and use the correct proportions of each ingredient. Similarly, with bus termination, you need to use the correct impedance value to achieve optimal performance. Failing to do so can result in a system that's as unreliable as a poorly baked cake!
Furthermore, remember that termination is just one piece of the puzzle. Other factors, such as cable quality, connector integrity, and proper grounding, also play a significant role in the overall performance of the bus system. A holistic approach to system design and maintenance is always the best strategy.
And finally, if you're not sure what you're doing, don't be afraid to seek expert help. There are plenty of experienced engineers and technicians who can assist you with troubleshooting and optimizing your bus system. Sometimes, a little professional guidance can save you a lot of time, money, and frustration. Good luck!
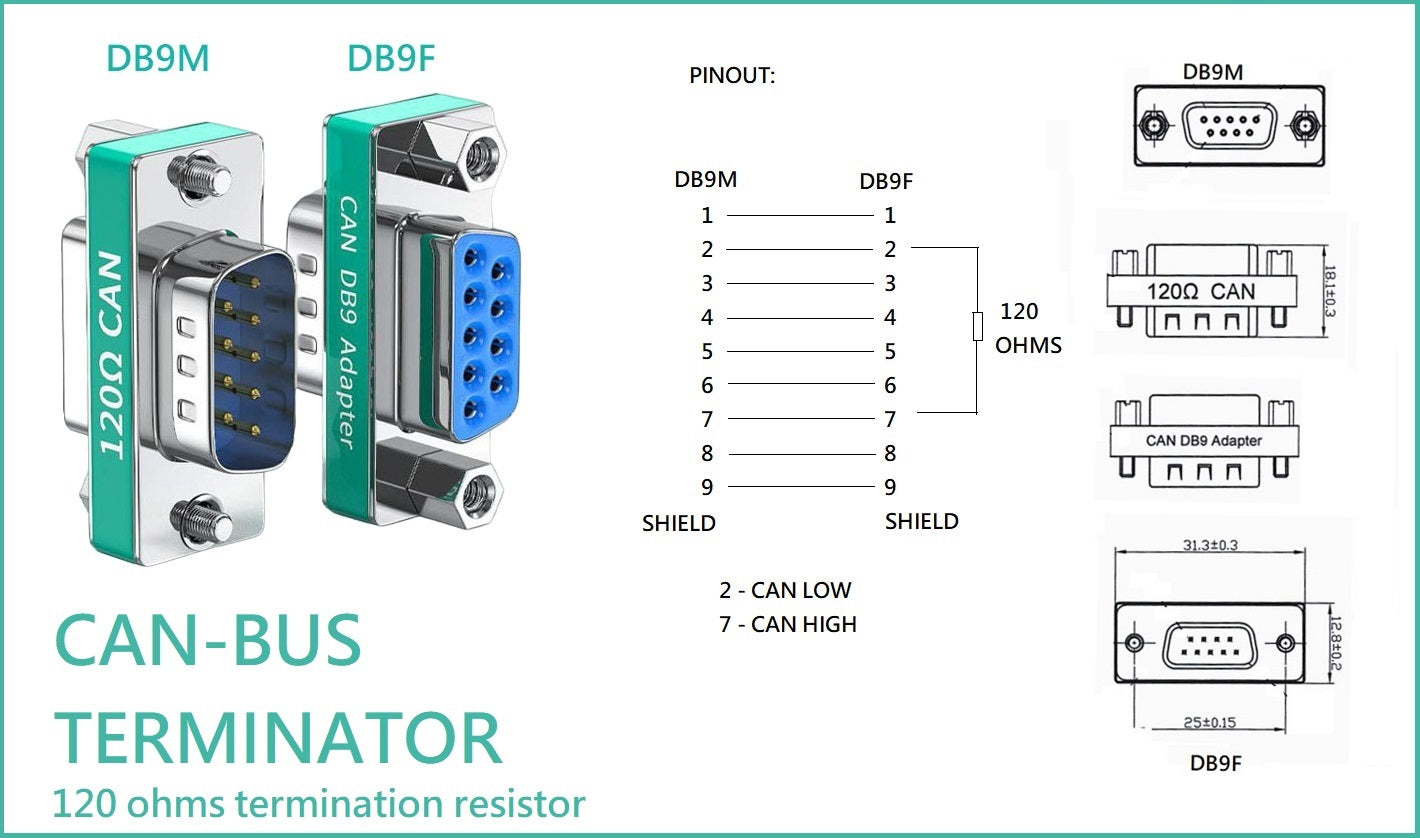
DB9 Male To Female Builtin 120 Ω (OHM) CAN Bus Terminating Resistor
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered!
Q: Can I just measure the impedance of the bus with a multimeter and choose my termination resistor accordingly?A: Sadly, no. A multimeter isn't designed to measure impedance accurately at the high frequencies used in bus systems. You need specialized equipment, such as a network analyzer, to get a reliable impedance measurement. And even then, it's generally best to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for termination.
Q: What happens if I use a termination resistor with a slightly different impedance value, like 58 ohms instead of 60?A: While a small deviation might not cause immediate catastrophic failure, it can still negatively impact signal integrity. Even a few ohms difference can increase signal reflections and lead to intermittent errors. It's best to stick to the specified impedance value as closely as possible.
Q: Do I always need a termination resistor at both ends of the bus?A: Not always. The number of termination resistors required depends on the specific bus topology and signal characteristics. Some buses require termination at both ends, while others only need it at one end. Again, consult the documentation for your specific system to determine the correct termination strategy.